[ad_1]
The Dencun upgrade has benefited layer-2 solutions, yet some experts are concerned about their complexity and potential risks.
On Mar. 13, the much-anticipated Dencun upgrade went live on the Ethereum (ETH) mainnet, promising enhanced scalability and reduced transaction fees for layer-2 (L2) networks.
Dencun incorporates nine Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), including data blobs via EIP-4844, refining Ethereum’s execution and consensus layers.
Layer 2 platforms have emerged as the biggest winners from Ethereum’s Dencun upgrade. For example, there was a notable increase in user activity on Base after the upgrade. The surge is primarily attributed to reducing Base’s transaction fees, making them much lower than Ethereum’s main layer fees.
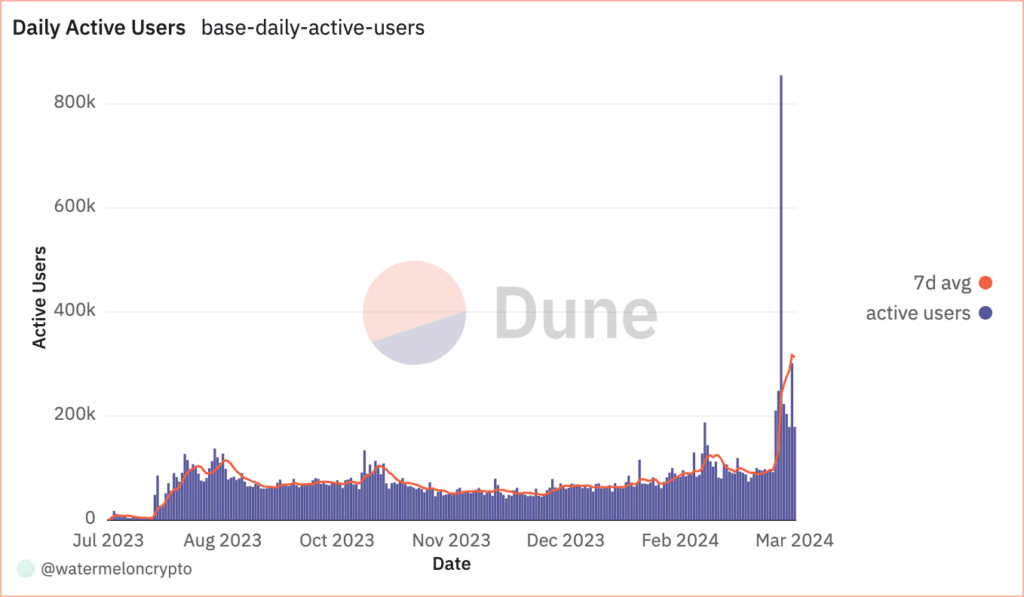
Yet, recent reports suggest that the fee reductions won’t benefit Ethereum mainnet users directly. If users want to take advantage of the fee change right away, they’ll have to compromise on how decentralized and secure their transactions are by using L2 solutions instead of sticking with Ethereum directly.
The community’s response to Dencun has also been mixed, with some expressing skepticism about the effectiveness of L2 solutions.
A recent Reddit thread highlights concerns about L2 usage, its user-friendliness, and its adoption potential.
Even Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin has voiced reservations In February 2024, acknowledging the inherent risks posed by L2 adoption.
In a series of tweets, Buterin emphasized the trade-offs between L1 and L2 bug risks, questioning the prevailing notion of simplifying layer-1 (L1) at the expense of intricate L2 solutions.
He questioned if making L1 simpler is really worth it when considering all the complications and potential risks that come up at the L2 level.
Are L2s truly safe for the system? Let’s delve into these risks and their potential implications for Ethereum and other blockchain ecosystems.
New heights, new risks
Over the years, Ethereum (L1) has been criticized for being slow and expensive, hindering its potential to serve as a foundational layer for various crypto-based applications.
The Dencun upgrade has enhanced Ethereum’s capability to support L2 solutions more effectively by introducing features like “blobs”. The end goal with this upgrade is to hit 100,000 transactions per second (TPS). The Dencun upgrade is focused on rearchitecting Ethereum to better support L2 solutions by prioritizing scalability through rollups.
Before the upgrade, the cost of sending ETH via these rollups ranged from $0.15 to $0.70. However, according to data from L2fees.info, this cost has come down to less than $0.01.
These lower fees on rollups following the Dencun upgrade could drive greater adoption of Ethereum-based applications over time.
However, this adoption comes with several risks and uncertainties that could hamper blockchain growth if things go wrong.
The risk of concentrated power
One of the foremost risks associated with L2 scaling solutions is the potential for centralization.
Picture a decentralized network like a vast web, with power distributed across many nodes. In an ideal scenario, no single entity holds too much control, ensuring fairness and transparency.
However, as L2 solutions evolve, there’s a growing concern that power might become concentrated in the hands of a few.
In essence, entities known as sequencers bundle transactions and transport them to the main L1 blockchain. If just a handful of entities control these sequencers, it creates a single point of failure.
This concern isn’t merely theoretical. In reality, many L2 networks rely on centralized sequencers. These entities, whether intentionally or not, hold significant sway over the network. They can dictate transaction order, potentially censoring certain transactions or even manipulating the system for their gain, opening the door to abuse and eroding trust in the network.
Complexity and technical risks
Another significant risk associated with L2 scaling solutions is complexity. At its core, L2 scaling aims to streamline transaction processing and enhance blockchain scalability. However, achieving these goals requires overcoming a series of technical challenges.
One of the primary complexities lies in designing and implementing L2 protocols. These protocols dictate how transactions are processed and verified off-chain before relaying to the main Ethereum blockchain. These protocols require a deep understanding of cryptography, consensus mechanisms, and network architecture.
Moreover, L2 solutions come in various forms, including sidechains, state channels, and rollups, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right solution requires careful consideration of factors like security, scalability, and user experience.
Сomplexity doesn’t stop at the design phase—it permeates every aspect of L2 implementation. From setting up infrastructure to managing network nodes, every task demands attention to detail. Even minor missteps can have far-reaching consequences, jeopardizing the security and stability of the entire network.
Furthermore, the user experience of L2 solutions can be less than intuitive, and users may struggle to deposit funds and withdraw them back to L1, serving as a barrier to widespread adoption for everyday users.
Security risks
Some L2 solutions don’t have robust fraud-proof mechanisms. Fraud proofs are crucial for verifying the accuracy of transactions on L2 and providing users with assurances regarding fund security. Without them, users may be exposed to risks like double-spending attacks or invalid transactions.
Additionally, L2 solutions rely on separate sets of validators and consensus mechanisms. Incompatibilities between protocols and technologies used in various L2 networks can create vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit to compromise transaction security and the integrity of the broader blockchain ecosystem.
What lies ahead
Various industry experts share a mix of optimism and caution regarding Dencun’s future implications.
On one hand, the immediate effect of lowering transaction costs and enhancing scalability is widely celebrated. For instance, StarkNet observed a 99% reduction in fees, and Optimism’s fees dropped to mere cents.
However, the experts are concerned about the long-term effects of the upgrade, particularly regarding the potential rise in demand for blobs, which could lead to costs increasing again, and the centralization risks associated with L2 solutions.
To tackle these centralization issues, they suggest various solutions, including shared and direct decentralized sequencers. Shared sequencers function across multiple L2 networks, encouraging interoperability and flexibility.
On the other hand, direct decentralized sequencing permits each L2 to operate with its own set of sequencers, offering greater customization and autonomy.
Hence, the future of Ethereum’s scalability and efficiency rests on the ecosystem’s ability to balance immediate benefits with long-term sustainability, ensuring that advancements like Dencun continue to support the blockchain’s growth and accessibility.
[ad_2]
Source link
